What is CBN?
Summarize

If you’re familiar with cannabis, then you probably know a bit about CBD benefits and THC. The two most popular cannabinoids produced by the cannabis plant, CBD and THC aren’t the only cannabinoids that you can supplement with. CBN (cannabinol) is another cannabinoid that has medicinal qualities.
Only found within the cannabis plant, CBN vs. CBD is located in large quantities in its source when the plant or product is older. If you want to learn more about this beneficial cannabinoid, read on.
Table of Contents
What Is CBN?
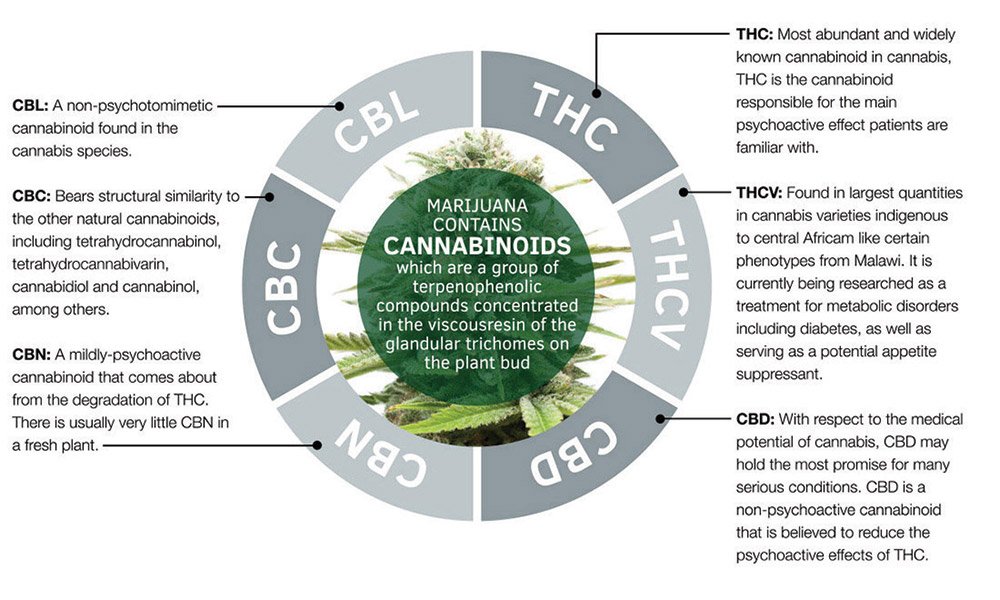
Cannabinol (CBN) is a cannabinoid found in the cannabis plant. Cannabinoids are extracted from the hemp plant, a specially cultivated type of cannabis that contains no more than 0.3% THC dry weight. The hemp plant has more than 150 identified phytocannabinoids, and it is believed there are many more. CBN is one of the many phytocannabinoids and is experiencing growing interest among researchers.
CBN is primarily formed as a result of the biosynthesis of delta-9 tetrahydrocannabinol (THC), but relatively recent research has discovered a more complex process occurs. The path of CBN production is that CBGA is synthesized into CBDA and THCA. The THCA produces THC through decarboxylation and CBNA through oxidation. THC exposed to light, heat and air breaks down into CBN. CBNA also breaks down through decarboxylation and becomes CBN.
So, the degradation of the hemp plant produces CBN from CBNA and THC. Higher amounts of CBN are found in dry, aged cannabis plants as a result of the THC degradation process.

What Is CBN Oil?
CBN oil is extracted from hemp plants. The most common method is supercritical CO2 extraction, which uses pressurized carbon dioxide, so no solvents are necessary. The extracted CBN oil is then heated and cooled, removing impurities.
Another common extraction method is steam distillation. This is also a solvent-free process in which hot water vapor is passed over the hemp plant material. The hot water causes the plant material to evaporate and release its essential oils. The oil is then filtered to remove any impurities.
CBN oil is used in various products. Two spectrums are used in products with a CBD-to-CBN ratio.
- Full spectrum CBD contains all of the cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids in the hemp plant.
- Broad spectrum CBD contains the same cannabinoids, but THC is removed during processing.
How Does CBN Work?
Still being studied, scientific research suggests CBN has a low affinity for CB1 receptors and binds mainly to CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. The CB2 receptors are primarily present in peripheral organs and are involved in the immune system. The CB1 receptors are concentrated in the brain and central nervous system; some are found in the organs and nerves.
CBN is mildly psychoactive since it forms from THC. However, there is not enough CBN in hemp products to cause intoxication. CBN is not fully understood because the research is scarce, and most studies have been animal studies. The research that has been done has found that CBN may have therapeutic effects.
CBN Potential Benefits
By working through the endocannabinoid system at the cellular level, CBN may provide the following benefits.
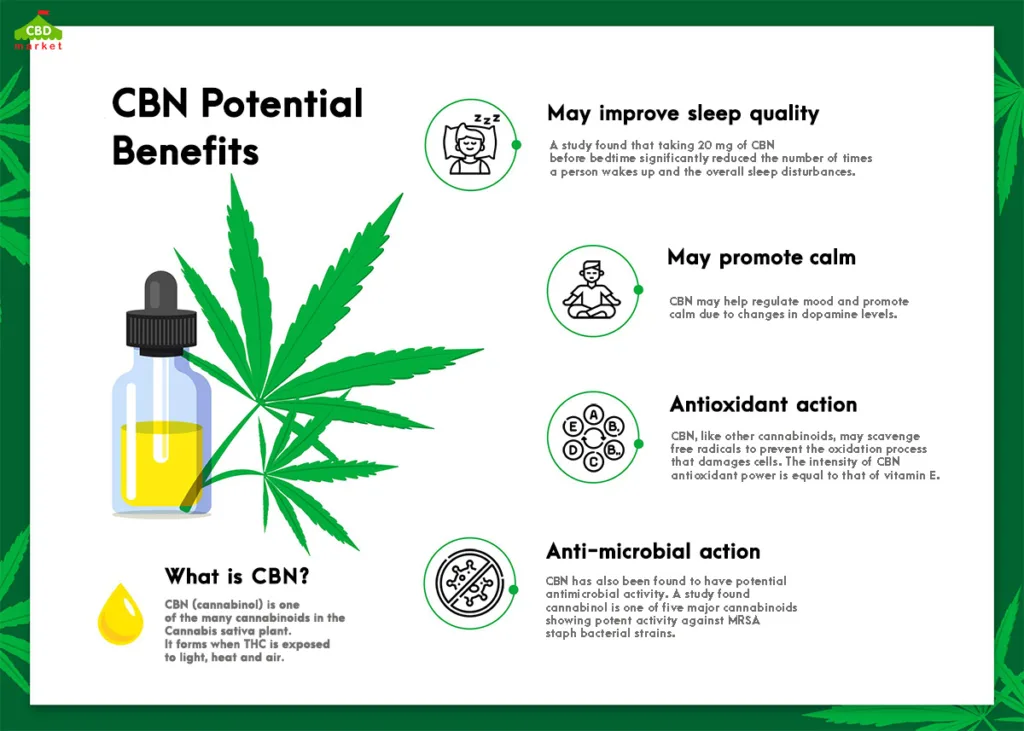
1. Stimulating Appetite
Most of the compounds within cannabis can spark a person’s appetite a bit. Rodent studies have determined that consuming CBN will increase the amount of food that is eaten. For people who are trying to avoid THC because of its psychoactive effects, CBN is a great alternative.
There are many reasons you might want to stimulate your appetite. There are some prescription medications that can diminish a person’s taste, leaving them very vulnerable to things like infection or illness.
2. Neurodegenerative Prevention
CBN can also act as a protecting agent for our nervous system and brain. Studies have been conducted on the effects of CBN. More research is needed on human consumption, but CBN may have some potent benefits.
3. Natural Sedative

Some people believe that CBN can be used as a natural sedative. It looks as though CBN is more beneficial for this purpose when it is used in combination with THC. These two compounds, together with terpenes, can cause relaxation and sleepiness.
A lot of people who take only CBN don’t find that it affects their ability to stay awake or focus. We do understand one thing. The number of terpenes that are found in cannabinoids will increase as the product ages. These terpenes have sedating effects.
Researchers have also found that CBN taken with some THC may enhance the effects of THC. What is not known is how CBN and terpenes may interact. Terpenes are believed to have therapeutic benefits, some of which are similar to CBN.
Does CBN Work for Sleep?
CBN is called the “sleep cannabinoid” because products made with CBN have helped people fall asleep and stay asleep, according to primarily anecdotal evidence.
There is a study that investigated the effects of CBN alone and in combination with CBD. The conclusion was that taking 20 mg of CBN each night could improve sleep disturbance.
So, most of the evidence that CBN works for sleep improvement is based on users’ reports. However, there are studies indicating CBN may enhance the sedative properties of THC through the interaction with the endocannabinoid system.
What Is The Difference Between CBD and CBN?
While the majority of research is going towards understanding THC and CBD more, CBN has been researched to some degree. A CBD and CBN supplement can act as a potent antibacterial compound. When tested on MRSA bacteria strains, CBN found it very useful.
It’s a bacteria that is usually very difficult to treat because of its antibiotic resistance. It can cause reoccurring symptoms that continue for months or even years.
How to Buy CBD and CBN Oil Products?
You’re not going to find a lot of CBN within a fresh cannabis plant. You’ll find high quantities of it in an older cannabis plant. More specifically, a cannabis plant that has been exposed to high levels of oxygen will have higher levels of CBN. CBN comes from THC when it is oxidized.
There are many CBD brands that isolate CBN for consumption purposes. Right now, you’ll usually find CBN in the form of tinctures, capsules, gummies and isolate powder. They typically come in various doses, so you can see if you like their effect on your body before taking a large dose daily.
FAQs
Can You Take CBN Every Day For Sleep?
CBN is safe to consume, and no adverse effects have been reported at this point. In fact, there are no known side effects. However, if taking it for the first time, it is advisable to start with a low dose and increase the dosage after determining how CBN affects you.
What Works Better For Sleep: CBD, CBN or Melatonin?
Melatonin is a popular supplement for improving sleep. Normally, the body produces the melatonin hormone on a 24-hour circadian cycle. It is produced right after dark, peaks in the early morning hours and is significantly reduced during the daylight hours. When this cycle is disrupted, so is sleep quality. Melatonin is taken to support the circadian rhythm.
It is beneficial for many people, but it has drawbacks. Most commercial melatonin products are made synthetically through a complex chemical process. The primary issue with melatonin is that it should not be taken nightly as the primary sleep aid for more than one or two months.
If you are looking for a natural sleep aid compound, CBD or CBN are preferred choices. CBD may help with sleep by exerting a calming effect on the central nervous system.
CBN has demonstrated it may be a powerful sedative. The studies to date have also found that the effects are amplified when combined with THC, likely due to the entourage effect. A full spectrum CBD product with additional CBN will contain a low and legal amount of THC.
There is a placebo-controlled study in progress that is assessing CBD effects on sleep when individuals with sleep issues take either 30 mg or 300 mg of CBN each night. This is an important study because it is a human trial.
What Is CBN Good For?
Despite the limited research, CBN has shown it may be suitable for many things. It may act as a natural sedative for improved sleep quality, offer potential protection from neurodegeneration, stimulate appetite, and deliver antioxidants. Much more will be learned about CBN as more placebo-controlled clinical trials with humans are conducted.
What Is CBN Isolate?
CBN isolate is pure CBN. The extract undergoes additional processing to remove all other cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids. It is sold in powder form and used in otCBN products, including gummies, tinctures and capsules.
At the Result
With any cannabis-based product, you’ll want to take CBN in a low dose and work your way up from there based on your side effects and results. If you have already been taking CBD or another cannabinoid, you may be able to find a full-spectrum product that contains various cannabinoids in one dose.
It’s a great way to reap these powerful components’ benefits. Just keep an eye on the THC content. Many people like to utilize cannabinoids for their healing properties, but they don’t like the psychoactive effects that you experience when THC, CBD, and CBN are present.
It’s especially true if you are working in a field that requires you to pass a drug test on occasion. Always research a cannabinoid thoroughly before you start taking it daily. You want to make sure that this will be the right choice for your health regimen and lifestyle. Compare CBNvs CBD to see what option is best for you.
Sources
- InMed Pharmaceuticals. Cannabinol 101: The Science of Cannabinol (CBN)
https://www.inmedpharma.com/media-news/cannabinol-101-the-science-of-cannabinol-cbn/ - BMJ Open. (2023). Cannabinol (CBN; 30 and 300 mg) effects on sleep: protocol for a randomised, double-blind, placebo-controlled, cross-over, three-arm, proof-of-concept trial. 13(8): e071148. doi: 10.1136/bmjopen-2022-071148. PMCID: PMC10450062. PMID: 37612115.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC10450062/ - InMed Pharmaceuticals. InMed Pharmaceuticals Inc. Announces Results from a Phase 2 Clinical Trial in Epidermolysis Bullosa
https://www.inmedpharma.com/news_release/inmed-pharmaceuticals-inc-announces-results-from-a-phase-2-clinical-trial-in-epidermolysis-bullosa/ - Hayes Wong, Brian E Cairns. Cannabidiol, cannabinol and their combinations act as peripheral analgesics in a rat model. Arch Oral Biol. 2019 Aug;104:33-39. doi: 10.1016/j.archoralbio.2019.05.028. Epub 2019 May 28. PMID: 31158702.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/31158702/ - Rishi K Somvanshi, Shenglong Zou, Salam Kadhim, Sapna Padania, Eric Hsu, Ujendra Kumar. Cannabinol modulates neuroprotection and intraocular pressure: A potential multi-target therapeutic intervention for glaucoma. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2022 Mar 1;1868(3):166325. doi: 10.1016/j.bbadis.2021.166325. Epub 2021 Dec 16. PMID: 34921975.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/34921975/ - Nuanying Zhong, Dongping Li, Bo Wang, Olga Kovalchuk, Igor Kovalchuk. Biocatalysis and Agricultural Biotechnology. 2023. doi: 10.1016/j.bcab.2023.102627.
https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S1878818123000282 - Salk Institute. Protecting brain cells with cannabinol: Scientists uncover novel cannabinol neuroprotective properties and discover promising cannabinol analogs for potential future therapeutic application in traumatic brain injury, Alzheimer’s, and Parkinson’s. Science News from research organizations. 2024 Apr 17.
https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2024/04/240417182826.htm - I G Karniol, I Shirakawa, R N Takahashi, E Knobel, R E Musty. Effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol in man. Clinical Trial Pharmacology. 1975;13(6):502-12. doi: 10.1159/000136944. PMID: 1221432.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1221432/ - Nirmal Joshee, Sadanand A. Dhekney, Prahlad Parajuli, Destinney Cox-Georgian, Niveditha Ramadoss, Chathu Dona, Chhandak Basu. Therapeutic and Medicinal Uses of Terpenes. Medicinal Plants. 2019 Nov 12;333–359. doi: 10.1007/978-3-030-31269-5_15. PMCID: PMC7120914.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7120914/ - Nicoleta Mirela Blebea, Andreea Iulia Pricopie, Robert-Alexandru Vlad, Gabriel Hancu. Phytocannabinoids: Exploring Pharmacological Profiles and Their Impact on Therapeutical Use. Int J Mol Sci. 2024 Apr; 25(8): 4204. doi: 10.3390/ijms25084204. PMCID: PMC11050509. PMID: 38673788.
https://psycnet.apa.org/fulltext/2024-14146-001.html - Marcel O. Bonn-Miller, Matthew T. Feldner, Teah M. Bynion, Graham M. L. Eglit, Megan Brunstetter, Maja Kalaba, Ivori Zvorsky, Erica N. Peters, Mike Hennesy. A Double-Blind, Randomized, Placebo-Controlled Study of the Safety and Effects of CBN With and Without CBD on Sleep Quality. Experimental and Clinical Psychopharmacology. 2024; 32(3): 277-284. doi: 10.1037/pha0000682.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC11050509/ - Scott Shannon, Nicole Lewis, Heather Lee, Shannon Hughes. Cannabidiol in Sleep: A Large Case Series. Perm J. 2019;23:18-041. E-pub: 01/07/2019. doi: 10.7812/TPP/18-041.
https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6326553/pdf/18-041.pdf - Woolcock Institute of Medical Research. ClinicalTrials.gov ID NCT05344170.
https://clinicaltrials.gov/study/NCT05344170 - I G Karniol, I Shirakawa, R N Takahashi, E Knobel, R E Musty. Effects of delta9-tetrahydrocannabinol and cannabinol in man. Clinical Trial Pharmacology. 1975;13(6):502-12. doi: 10.1159/000136944. PMID: 1221432.
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/1221432
Share this post





0