What is THC?
Summarize
THC is a cannabinoid that still evokes images of drug users getting high on marijuana for recreational purposes. However, researchers are finding that taking THC in the right amount and with other cannabinoids in a full-spectrum CBD product may provide significant benefits for some people. The first step is understanding where THC comes from, how it is legally included in products, and its effects.

TL;DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read):
THC is getting a lot of attention because it is found in full spectrum CBD and is used for medicinal purposes as medical marijuana. THC is extracted from the cannabis plant. Industrial hemp is a specially cultivated federally legal cannabis plant with no more than 0.3% THC in dried plant material. THC is intoxicating and psychoactive when taken in higher amounts. Full spectrum CBD has no more than 0.3% THC and all the cannabinoids, terpenes, and flavonoids the cannabis plant offers. It is a way to enjoy the entourage effect for well-being without risking getting high.
Table of contents
What is THC?
The acronym THC means Tetrahydrocannabinol. It is a psychoactive cannabinoid in the cannabis plant. THC is only one of 113 cannabinoids found in this plant. Cannabis refers to the Cannabis sativa plant, which contains more than 540 different substances, so the word “marijuana” refers to the plant with the most THC. Cannabis plants specially cultivated to produce 0.3% THC or less are called industrial hemp plants to differentiate marijuana and plants used to make CBD products, which may contain some THC.
THC and CBD are the most abundant cannabinoids in the Cannabis sativa plant and are often referred to as the major cannabinoids.
How Does THC Affect the Body and Brain?
According to the National Institute on Drug Abuse, cannabinoid receptors in the body and brain are related to actions such as memory, thinking, pleasure, coordination, and perception of time. When THC binds with these various receptors, they become activated to a greater degree. Other cannabinoids are non-psychoactive. They even can block the effects that THC can cause.
THC in reasonable amounts will stimulate cells in the brain to release the chemical dopamine. It will create a very pleasurable feeling. When taken in more significant numbers, hallucinations, and delusional behavior can occur. At higher levels, the differences between CBD and THC are apparent. The impairment of specific functions may be noticeable even after the initial high has worn off. Once ingested, THC will kick in around 10 to 30 minutes later. It can be hours before a person will feel like themselves again.
The use of THC-free cannabinoids is something many people can do throughout the day because of the non-psychoactive effects of these other compounds. Other cannabinoids and terpenes that are naturally found in the hemp and cannabis plants can often counteract these effects if you are utilizing a full-spectrum product.
How Was THC Discovered?

You may be surprised to learn that an ancient man in China was buried around 750 BC with 800 g of the cannabis plant containing a high amount of THC. Over thousands of years, evidence has been found that human ancestors across continents used the Cannabis sativa plant for food, nets, and ropes, and the seeds were used for oil. There are early records of humans using cannabis for medicinal purposes.
Before 1964, some scientists had extracted a mixture of Δ-8 and Δ-9 THC but had not isolated THC. It was not until 1963 that the Raphael Mechoulam lab isolated CBD and, in 1964, isolated Δ-9 THC in the cannabis plant for the first time.
Over the next couple of decades, researchers focused on learning how THC interacts with the body. In 1988, the Endocannabinoid System (ECS) was discovered by researchers at the Saint Louis University School of Medicine. The ECS has various receptors regulating the body’s systems, keeping it balanced. With the discovery of the ECS system, the researchers learned that cannabinoids interact with two central receptors called CB1 and CB2. It is now known that the ECS has three primary components: endocannabinoids (naturally produced cannabinoids), receptors, and enzymes that break down cannabinoids once they are no longer working.
Different Types of THC
Where does THC come from? THC is found in the cannabis plant’s dried leaves, flowers, stems, and seeds. The THC complete word is Tetrahydrocannabinol, but there are different types of THC.
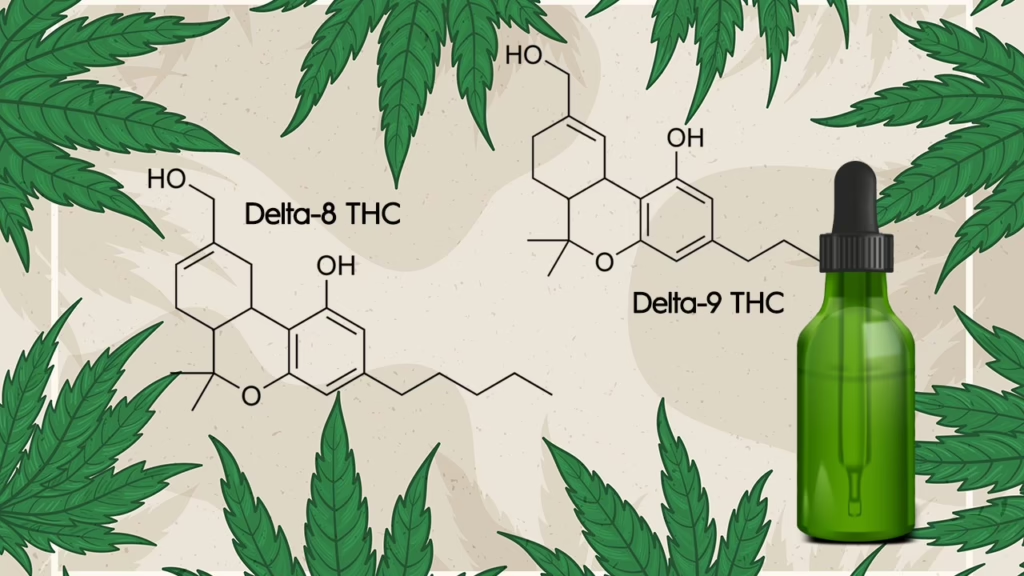
Δ-9 THC
Δ-9 THC is a major cannabinoid in the cannabis plant. This natural chemical, the most abundant cannabinoid, has psychoactive or mild-altering properties. The effects of Δ-9 THC depend on factors like the THC dosage, the way the THC is consumed, and personal characteristics like body chemistry and tolerance.
Δ-8 THC
Δ-8 THC is also in the Cannabis sativa plant but in much less quantity than Δ-9 THC. As a result, Δ-8 THC is usually extracted from the industrial hemp plant’s CBD through a chemical synthesis manufacturing process. Δ-8 is also psychoactive, like Δ-9 THC. There are concerns about the use of Δ-8 THC by consumers because of the use of chemicals during manufacturing that may contaminate the product.
THCA
THCA is the acronym for tetrahydrocannabinolic acid, a precursor to THC. It is found in large amounts in the flowers and leaves of the Cannabis sativa plant in its acidic form. Before heating, THCA is non-psychoactive. When the cannabis plant is dried and heated, THCA is slowly decarboxylated. Dried plant material heated during use, like smoking, also leads to decarboxylation. When heated, THCA becomes the psychoactive Δ-9 THC. As THCA, the cannabinoid precursor is not psychoactive.
THCV
THCV is naturally found in small amounts in some Cannabis sativa plants. Growers cultivate high-THCV strains, but much THCV is not extracted directly from the plant. Instead, a complex chemical conversion process starts with converting CBD. It has a molecular structure similar to THC but unique properties. THCV is not intoxicating (high) but has psychoactive effects and is being studied for potential effects like decreased appetite.
THCP
Recently discovered in 2019, THCP (Tetrahydrocannabiphorol) has a similar structure as Δ-9 THC with one difference. It has a longer alkyl chain, a key factor in cannabinoid biological activity, particularly the CB1 cannabinoid receptor. Compared to Δ-9 THC, THCP has a stronger binding affinity for CBD receptors. THCP is more potent as an intoxicating and psychoactive cannabinoid than Δ-9 THC. It has a high binding affinity to CB1 and CB2 receptors in the ECS system.
Δ-10 THC
Δ-10 THC was discovered in the 1980s. It is usually derived from hemp-derived CBD and not directly from the hemp plant because only trace amounts are in it. This means chemicals are used to extract Δ-10 THC. Δ-10 THC does activate the CB1 and CB2 receptors, so it has some intoxicating and psychoactive effects but much less than Δ-9 THC. Most information about this cannabinoid is currently anecdotal, with people saying it makes them feel more focused and euphoric.
It is quite likely there are more types of THC yet to be discovered. One crucial fact is that Δ-8 THCO and Δ-9 THCO are synthetic forms of Δ-8 THC and Δ-9 THC. The Drug Enforcement Agency (DEA) has made it clear that Δ-8 THCO and Δ-9 THCO are Schedule 1 controlled drugs because neither occurs naturally in hemp. They are synthetic derivatives.
Beneficial Uses of THC Oil
Cannabis has been used for medicinal purposes for over 3,000 years now. In recent years, many states in the U.S. have begun to legalize marijuana. There are even states that are allowing for the recreational use of marijuana. There are both natural and chemically produced forms of THC. The chemical versions tend to be approved by the FDA and used for various medical purposes. Of course, it is essential to start a THC routine with the help of a medical professional. It will ensure that you are not going to have any interactions with other medications that you are taking. You will also receive advice on the correct dose to start with. While THC can be beneficial, it can also be dangerous if you aren’t using the right kind or the right amount.
Are There Risks Associated with THC Use?
Many people use marijuana. While it has some beneficial medical benefits, it can also have some adverse effects when not handled properly. For example, people with mental health issues may have a relapse of their condition if they use a product with THC.
Aside from mental health effects, impaired motor skills are something that is a danger to oneself and the people around them.
You can experience impaired driving when you are using THC. The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration recommends that you do not drive when you are trying THC for the first time. It can take up to three hours for your response. In the younger population, long-term use of THC can significantly affect brain development and function. It can include a decreased IQ, shorter memory function, and diminished cognition.
The National Highway Traffic Safety Administration recommends that you do not drive when you are trying THC for the first time. It can take up to three hours for your complete response. In the younger population, long-term use of THC can significantly affect brain development and function. It can include a decreased IQ, shorter memory function, and diminished cognition.
The scientists need research to understand the risks associated with THC use. You cannot get an overdose from other cannabinoids. Unfortunately, you can overdose on THC if you are not careful. It seems to be more familiar with the edible products on the market. The absorption rate is a bit different, and people consume more than they should be.
Microdosing THC
Microdosing THC refers to consuming minimal amounts of THC, anywhere from 1-5 mg per dose. Once again, the right amount and the number of times each day to microdose depends on factors like metabolism, health conditions, weight, and more. The idea is to experience the benefits of THC without getting high. Some studies found patients taking microdoses of cannabinoids experienced more positive effects than those taking higher doses. One option is taking low-potency CBD oils or tinctures.

FAQs
Is THC Legal?
Selling marijuana is not legal at the federal level, but several states approved drugs contain synthetic THC. The FDA lists natural and synthetic THC as a controlled Schedule I substance, meaning mere possession is illegal.
The story is different at the state level. Despite the federal law, most states have specific laws that allow the growing, cultivation, sale, possession, and distribution of marijuana. The gap between federal and state laws has caused a lot of confusion.
The federal 2018 Farm Bill allows the growth, sale, and use of specially cultivated cannabis plants designated as “industrial hemp.” The plants can only have 0.3% THC content in dry-weight plant material. This amount was established because taking 0.3% THC in products will not cause a high. The 2018 Farm Bill made the limited amount of THC and CBD legal by removing the hemp plant from the Substance I schedule.
What’s the Difference Between CBD and THC?
CBD and THC are both cannabinoids found in cannabis plants. There are two main differences. One is that CBD is non-psychoactive, while THC is the primary psychoactive cannabinoid in the cannabis plant. THC could get you high, while no amount of CBD will. The other difference is how cannabinoids work in the ECS.
THC has a strong binding affinity for CB1 receptors, which manage human systems like sleep and appetite. CB1 receptors are found in high levels in the brain and nervous system. THC can overwhelm the ECS, so you can get high on it.
CBD has a low affinity for binding to the CB1 and CB2 receptors. CB2 receptors are found mainly in the immune system. CBD interacts with the receptors differently than THC. Instead of binding, it interacts with receptors CB1, CB2, TRPV GPR55 and more, modulating the receptor activities. Its main action is on the CB2 receptors, so research has found it may have therapeutical effects. Studies have found that CBD acts as a negative allosteric modulator of the CB1 receptors, which means it may reduce the psychoactive effects of THC.

How Long Does THC Stay In The System?
Many factors influence how long THC stays in your system, including your metabolism, product potency, product form and frequency of use. Generally, THC is detectable in urine for up to a month, in saliva for 24 hours, in blood for 12 hours and in hair for 90 days.
How Long Does THC High Last?
Generally, a THC high will last 1-6 hours. However, once again, there are many influencing factors. For example, if you consume an edible with THC, the edible must be digested first before the THC effects begin. So, the peak effect in the bloodstream begins in about 3 hours, and the high may last six hours. If you use a tincture sublingually, the THC is absorbed much faster, so the high is 1-4 hours. Other factors impacting how long the THC high lasts are THC potency, your metabolism, when you last ate food and frequency of use.
What Do You Need if You Want to Try THC?
When starting any new supplemental regimen, it is essential that you do plenty of research so you know what you are getting yourself into. While various cannabinoids are very safe and beneficial, THC oil can be dangerous if you aren’t using it properly. Also, there are many different products on the market, such as CBD, which has no side effects and no dangers.
While various cannabinoids are very safe and beneficial, THC oil can be dangerous if you aren’t using it the proper way.
Take your time to think about what you are purchasing. Look at additional ingredients to ensure you aren’t consuming unwanted chemicals and additives.
Try to stay away from products that have used fertilizers and pesticides during the growth process. There are organic products from brands that provide you with their third-party testing. These tend to be your most reputable options.
Also, once you have taken your chosen product, pay attention to how it makes you feel. If you notice anything unpleasant or unsafe, stop taking the product right away and consult a medical professional.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK563174/
- https://www.nccih.nih.gov/health/cannabis-marijuana-and-cannabinoids-what-you-need-to-know
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7605027/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC1760722/
- https://www.neuroscienceinc.com/news/2020/one-of-your-bodys-best-kept-secrets
- https://www.fda.gov/consumers/consumer-updates/5-things-know-about-delta-8-tetrahydrocannabinol-delta-8-thc
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5731255/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5549534/
- https://jcannabisresearch.biomedcentral.com/articles/10.1186/s42238-020-0016-7
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6937300/ and https://cbdoracle.com/cannabinoids/thcp/
- https://sc.edu/uofsc/posts/2023/04/conversation_cannabis_derived_products.php
- https://us.eversheds-sutherland.com/NewsCommentary/Legal-Alerts/257006/DEA-confirms-Delta-8-THCO-Delta-9-THCO-are-schedule-I-controlled-substances-but-confusion-remains#
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1526590012000193 and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4165471/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5209363/
- https://onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1111/bcpt.13710
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC4621983/
- https://americanaddictioncenters.org/marijuana-rehab/how-long-system-body
- https://www.medicalnewstoday.com/articles/how-long-for-edibles-to-kick-in
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7324885/.
Share this post


0