What Are the Benefits of CBD Terpenes?
Summarize
CBD product descriptions mention terpenes. Full spectrum and broad spectrum CBD always have some terpenes, but even some isolate CBD products may have infused terpenes. Most plants contain terpenes and that includes the hemp plant, the legal cannabis plant that has less than 0.3 percent THC. Terpenes are known as aromatic compounds and flavor influencers, but researchers find terpene profiles may also support wellness through the entourage effect. In the following sections, terpenes are discussed based on current research.

TL;DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read):
Terpenes are bioactive compounds in plants that serve several purposes, including determining the fragrance. Terpenoids are naturally modified terpenes that develop when the plant material is dried and processed. Per clinical researchers, terpenes and terpenoids are believed to deliver health benefits and are being studied for their potential therapeutic value. CBD producers can add additional terpenes to CBD oil and other CBD products during processing to enhance the benefits people experience.
What Are Terpenes?
Terpenes are compounds that occur naturally in plants and are a major element of essential oils, the concentrated plant extract obtained during plant material distillation or other forms of processing. The plants that are common sources of terpenes found in CBD products include citrus fruits and cannabis plants. Hemp is a legal cannabis plant (Cannabis Sativa). Terpenes are responsible for the plant’s pigment, taste and fragrance and also serve as plant protectants. They are believed to have positive impacts on health and wellness.
Essential oils are concentrated liquids that are extracted from various parts of plants. Terpenes are aromatic bioactive compounds in essential oils. They occur naturally in the trichomes of the female cannabis plant’s flowers. Glandular trichomes are small sticky glands found on the surface of cannabis flowers. The trichomes produce a resin that contains the plant’s terpenes, cannabinoids and flavonoids. That resin is the essential oil.
CBD oil is extracted from the trichomes of the flowers. There are small amounts of trichomes in the hemp plant’s stems, seeds and leaves, but the largest amounts are in the hemp plant’s flowers.
Terpenes and Terpenoids: Are They the Same?
Terpenes are frequently called terpenoids, but they are not identical compounds based on chemical structures. In the most basic terms, terpenes are compounds that have a simple hydrocarbon structure. Terpenoids are oxygen-containing hydrocarbons that are modified terpenes. Terpenoids form during photosynthesis and the drying and curing of plant material. During the process, the terpene molecular makeup is changed.
In the plant, the terpenes account for the different plant aromas and contribute to the plant’s ability to inhibit microbial growth, attract pollinators and resist herbivores.
More than 120 (more are regularly identified) types of cannabinoids have already been discovered in the hemp plant, and cannabinoids contain terpenoids. Cannabinoids develop when olivetolic acid (OA) is alkylated (joined) with a terpenoid to produce CBGA which is the precursor of the hemp plant’s major acidic cannabinoids, i.e., THCA, CBCA, CBDA, etc. A decarboxylation process then converts the acidic forms to forms that can be active in the human body.
Major Terpenes in CBD Oil
There are more than 200 terpenes in the cannabis plant. Terpenes are classified based on the number of isoprene units in the molecule.
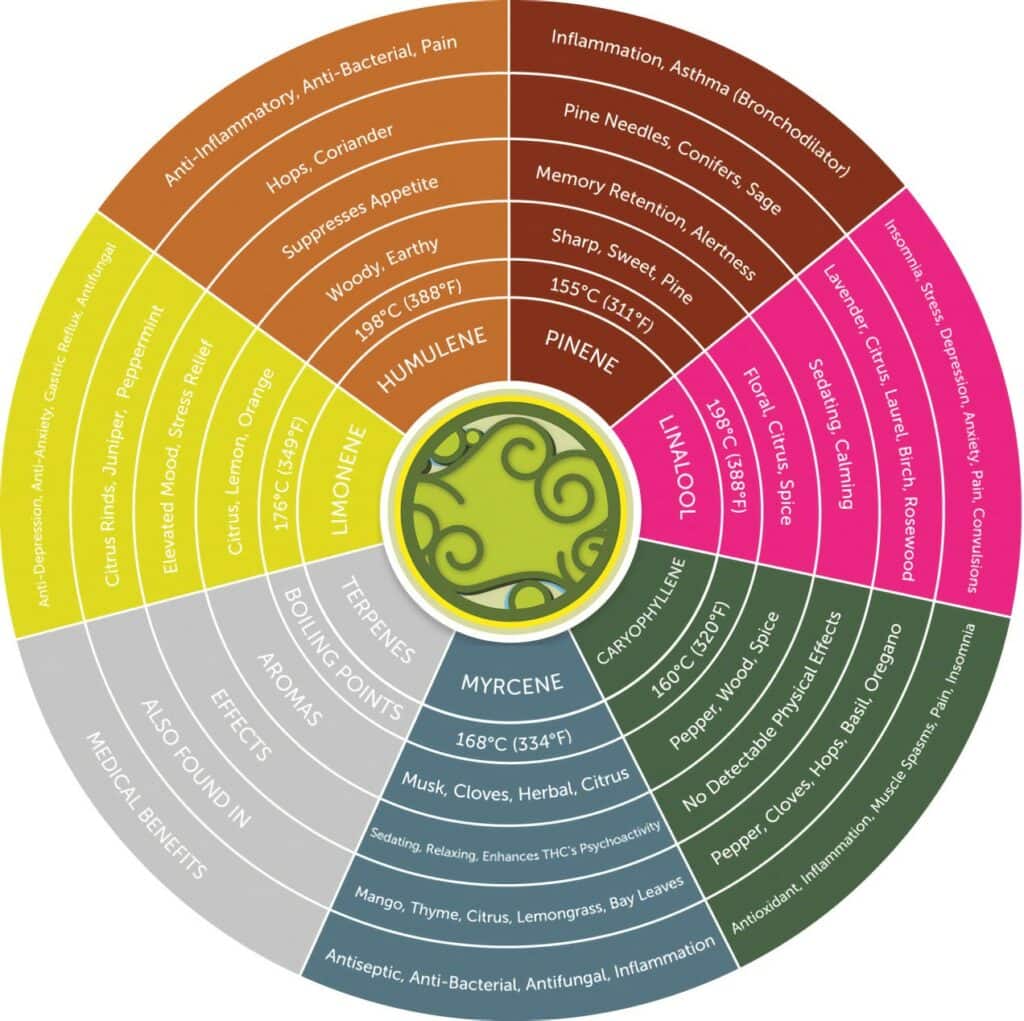
- Monoterpenes – two isoprenes, i.e., limonene, myrcene, terpinolene and pinene.
- Sesquiterpene – three isoprenes, i.e., humulene, B-caryophyllene and farnesol.
- Diterpenes – four isoprenes; cannabinoids are synthesized from the diterpene structure.
Following are some of the major terpenes (chemotype groups) in the hemp plant. Chemotypes are distinct chemical entities in plants.
- Myrcene is the most abundant terpene found in cannabis and is believed to contribute to lower expression.
- Pinene is believed to positively impact respiratory function, memory and mental alertness.
- Linalool is a terpene that may have relaxing properties and support the immune.
- Limonene is the second most abundant terpene found in cannabis, which may contribute to improved mood.
- B-Caryophyllene is believed to have anti-fungal, anti-bacterial and antioxidant properties; B-caryophyllene is the only terpene known to interact with the ECS (endocannabinoid system).
- Humulene – may contribute to reduced discomfort and may also have anti-bacterial properties.
- Terpinolene is believed to have antioxidant, antibacterial, and antifungal properties and is mildly sedative.
This is not a complete list, of course, but these are the major ones. Research is ongoing as it becomes clearer that terpenes and terpenoids can produce various effects.
Benefits and Effects of Terpenes
Terpenes are phytochemicals that researchers have been studying because they are believed to deliver therapeutic benefits and have the ability to improve general wellness. Aromatherapy is one of the most well-known benefits of terpenes, but there are many more.
Following are some potential benefits and effects of terpenes based on research to date.
- Increase energy
- Anti-fungal properties
- Anti-bacterial
- Anti-viral
- Muscle relaxation
- Reduce sore feelings
- Anti-oxidant properties
Terpenes are being studied for their ability to reduce stiffness because they are natural compounds and may one day help people reduce the use of prescription drugs. Some terpenes interact with cannabinoid receptors in the endocannabinoid system, like beta-caryophyllene, and help the body maintain balance (homeostasis).
Terpenes and the “Entourage Effect”
The entourage effect is the synergy achieved when two or more compounds work together to produce a greater impact than a single compound. Hemp terpenes improve CBD functionality by working together to produce excellent antioxidant activities.
Some terpenes are believed to enhance the effect of cannabinoids and produce a synergy that helps you feel more relaxed and have increased energy and improved focus. This is why many CBD products add cannabis terpenes and terpenes from other botanicals and fruits to CBD oils and edibles.
The entourage effect is the special relationship formed when terpenes, cannabinoids and flavonoids work together. One of the main reasons people buy full spectrum CBD is to enjoy the full entourage effect that comes with the hemp plant’s whole phytochemical profile.
Are Terpenes Safe?
Terpenes have been used in many products for decades, including cosmetics and lotions. Terpenes in CBD oil are considered safe. The only caution is that there may be some terpenes that people might be allergic to like the terpenes in grapefruit. Terpenes are not known to cause allergies directly but may trigger a mild allergic reaction when some people breathe in the aroma. Some people might experience skin sensitivities to certain terpenes.
Product Quality is Important
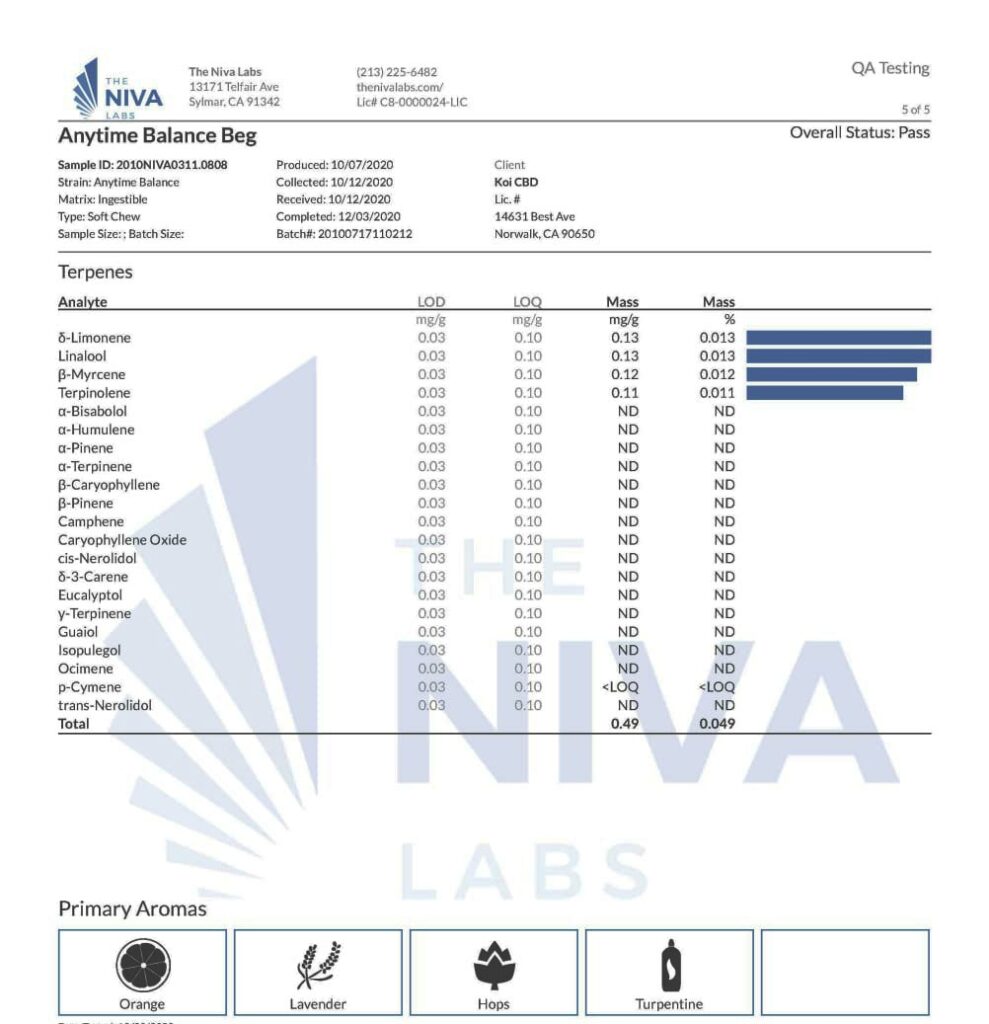
There is still a lot to learn about terpenes. For example, some terpenes are lost during the normal cannabis extraction process. That is why many CBD producers add terpenes during the production process. It also allows them to develop proprietary formulations that target specific effects. Many growing conditions influence the number of terpenes in the hemp plant. It is important to buy CBD oil from CBD retailers who maintain quality control standards from the type of hemp plants cultivated to the final packaging. Always review the Certificate of Analysis to determine the terpene profile of the CBD oil.
Sources
- https://www.niehs.nih.gov/health/topics/agents/essential-oils/index.cfm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7120914
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8488169/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9039924/
- https://www.thieme-connect.de/products/ejournals/abstract/10.1055/a-0828-8387
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2772566922000015#bib0021
- https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/abs/pii/S0021967320311389?via%3Dihub
- https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/23/5/1230
- https://www.karger.com/Article/FullText/509733
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fnut.2021.699666/full
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.583211/full
- systemhttps://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fpsyt.2021.583211/full
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7120914/
- https://www.mdpi.com/1420-3049/25/24/5792
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/35436102/
- http://www.znaturforsch.com/ac/v60c/s60c0821.pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8489319/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8414653/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/32234216/
Share this post


0