Should You Take CBD Oil Before or After Meals?
Summarize
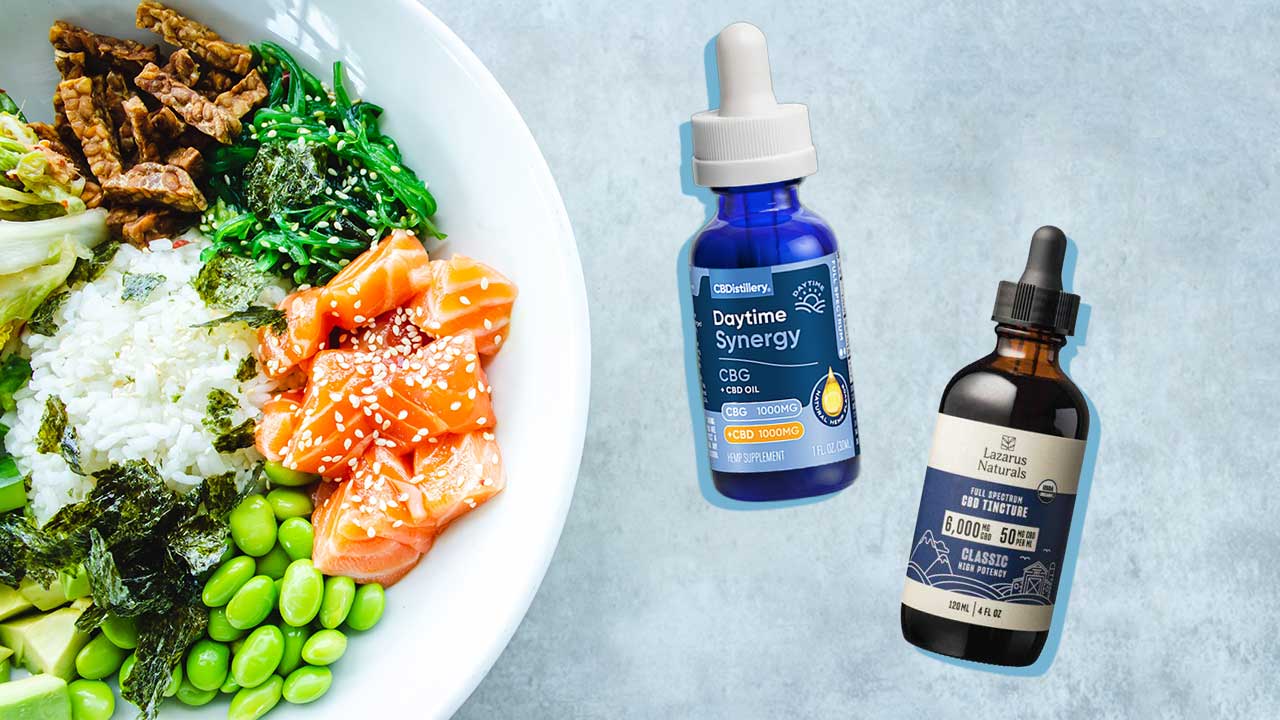

CBD oil is consumed in various ways, including as oil or tincture, capsules, edibles, gummies and in food. When consumed with food, there are benefits to taking CBD after eating fatty foods or eating CBD edibles with ingredients known to have healthy fats. Although you can take CBD oil at any time, using it after meals may provide the maximum benefits.
Table of Contents
How Does CBD Work in the Body?
The endocannabinoid system (ECS) is one of the more recent discoveries concerning the human body. The surprising discovery was how much the ECS regulates important bodily functions, including body temperature, immune responses, and more. The ECS is comprised of cellular receptors located in the brain and throughout the body, and the receptors process chemical signals as their regulatory process. The body produces endocannabinoids, molecules similar to cannabis plant molecules, to activate the receptors, so they regulate the various bodily functions mentioned.
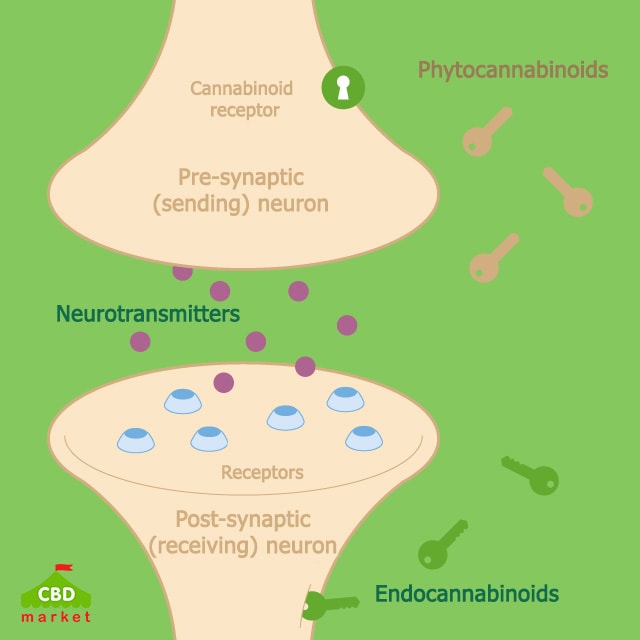
There are two main receptors called CB1 and CB2. The brain has more CB1 receptors than other kinds of receptors. CB1 receptors regulate the other neurotransmitters, helping them adjust as necessary to control things like hunger and body temperature. CB2 receptors are found mostly in immune tissues, so they assist immune functioning.
Activating CB2 receptors with cannabis (hemp plant) cannabinoids does not produce a high. Stimulating CB1 receptors does lead to experiencing a high. CBD does not bind directly with CB1 or CB2 receptors. It acts indirectly, and in that way, CBD influences how the receptors work. CBD is called an antagonist because it modulates the effects of stimulating the CB1 and CB2 receptors.
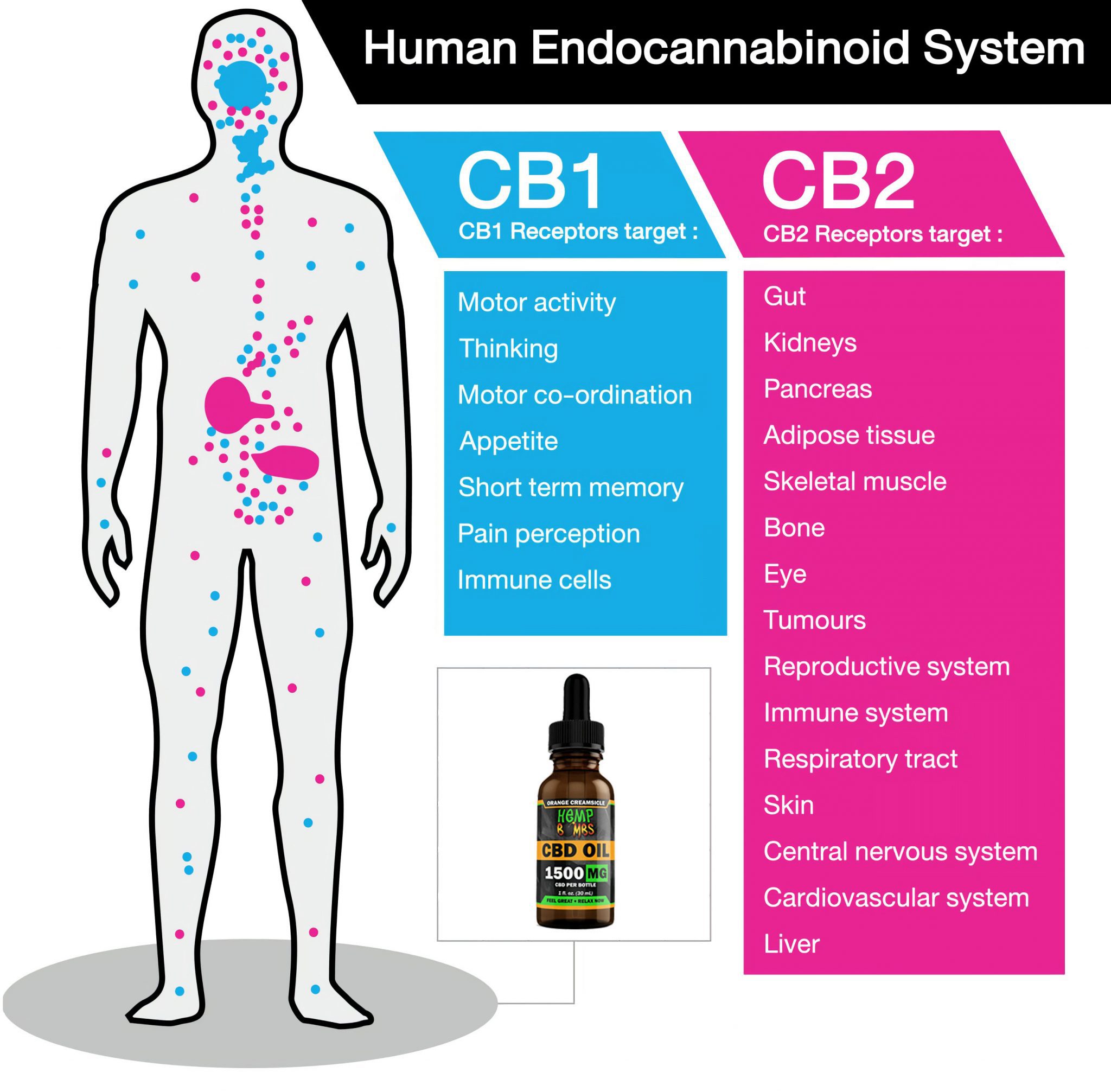
Medical research is ongoing to determine if CBD could be useful for doing things like hunger. Though more research is needed, there are labs and medical institutions regularly conducting clinical trials to determine exactly how CBD works in the body because CBD offers promise as potential drug therapy in the future.
Should You Take CBD Oil With Food?
Can you eat CBD oil? If so, should you take CBD oil with or without food?

A Singlecare survey found that 33 percent of Americans have used CBD at least once. Millions of people are already regularly using CBD, and many prefer taking CBD oil with or in food.
There are two things to understand about CBD consumption, either in a carrier oil or as CBD oil added to food.
- The first is bioavailability. The term bioavailability refers to the amount of CBD that enters the circulation system. The amount of CBD influences the effects experienced. Bioavailability also refers to how long it takes a substance to enter your circulation system.
2. The second term is “first-pass metabolism.” When you orally consume drugs, food, drinks or other substances by swallowing, they must go through the digestive system. As the substance is processed, some are metabolized by your body’s tissues before reaching the liver for processing into the circulation system and eventually the brain.
This process takes time, so any effects felt from swallowing CBD oil or consuming edibles are delayed. The one exception is that taking CBD oil sublingually bypasses the first-pass metabolism process and increases the amount of CBD that enters the system.
Swallowing CBD oil leads to low bioavailability for these reasons. Also influencing bioavailability is your personal metabolic rate and the way CBD is consumed, like in a capsule or in food.
Should you take CBD oil in food?
There is research that found taking CBD oil with high-fat foods can increase CBD bioavailability. One study reported that bioavailability can be increased four-fold by taking CBD with a high-fat and high-calorie meal compared to taking CBD on an empty stomach.
The reason is that cannabis cannabinoids are lipid-soluble, so taking the CBD oil with or in foods with dietary lipids like butter, whole milk or vegetable oil increases bioavailability. You can also take CBD oil mixed with oil like sesame oil to increase bioavailability. Researchers found the primary mechanism for the increased bioavailability is due to the transport of the CBD via the intestinal lymphatic system rather than the liver.
What Foods Work Best With CBD Oil?
The question then becomes the best high-fat foods to take with CBD oil combined with food. Some fats are good for you, and those are the fats you want to concentrate on. You do not want to eat a lot of fatty foods that lead to health problems. CBD cookies make a great snack and may contain high-fat ingredients, but you cannot live on cookies. Healthy fats are found in oils like sesame oil, coconut oil and MCT oil. Foods rich in healthy fats include:
- Fatty fish, like trout and salmon
- Nuts, like walnuts and almonds
- Avocado
- Dark chocolate
- Yellow yolk in eggs
- Hard cheese containing the most fat

If you love cookies, choose CBD edibles purposely made with healthy high-fat ingredients, like ones made with peanut butter and palm oil. The intentional choice of ingredients increases CBD bioavailability while helping you avoid consuming unhealthy fats.
The best time to take CBD oil is right after eating a meal because the CBD remains in your digestive system longer as your body processes the food. Taking CBD after eating food gives you the best chance of increasing bioavailability by four times, as mentioned earlier.
Do you swallow CBD oil? Yes, you can swallow it. You can also take CBD oil on an empty stomach. However, to maximize bioavailability, you would want to take a CBD tincture sublingually, so the CBD is absorbed directly into the bloodstream through the capillaries under the tongue. You hold the CBD oil under your tongue for 30-90 seconds before swallowing the oil.
Summary
You can take CBD with or without food, but your choice influences bioavailability. You want to achieve the highest bioavailability, so using CBD oil with food makes sense based on medical research to date. The research has found that CBD oil combined with food high in healthy fats increases the amount of CBD absorbed into your system. Taking CBD after a meal slows down absorption, which gives the CBD more time to reach your circulation system.
Sources
- https://www.health.harvard.edu/blog/the-endocannabinoid-system-essential-and-mysterious-202108112569
- https://www.researchgate.net/publication/6558573_Cannabidiol_displays_unexpectedly_high_potency_as_an_antagonist_of_CB1_and_CB2_receptor_agonist
- https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fphar.2018.01259/full
- https://www.singlecare.com /blog/news/cbd-statistics/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551679/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC7558665/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5009397/
- https://www.hsph.harvard.edu/nutritionsource/cheese/
Share this post


0