Benefits of CBD and THC Together in Full Spectrum CBD Products
Summarize

CBD and THC are the most abundant cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. These two natural cannabinoids offer benefits through their interactions with the human endocannabinoid system. Does CBD need THC to work? It does not, but the benefits of CBD, THC, and other natural compounds like terpenes, flavonoids, and minor cannabinoids may deliver an entourage effect that supports good health and wellness. Full spectrum CBD oil has some THC in it, making it easy to determine if taking both cannabinoids is a good choice to potentially meet your wellness needs, like deeper sleep or feeling some relief.

TL;DR (Too Long; Didn’t Read):
CBD and THC are the two primary cannabinoids in the cannabis plant. Full spectrum CBD oil is made with a whole cannabis plant extract so that consumers may enjoy an important benefit called the entourage effect. The entourage effect of CBD, THC and other plant compounds suggests the plant compounds perform synergistically when interacting with the endocannabinoid system. Research on CBD, a non-psychoactive cannabinoid, has found that CBD likely counteracts THC in terms of THC’s psychoactive effects. In addition, combining CBD and THC may increase the potential benefits of taking cannabinoids.
Table of Contents
What is CBD?
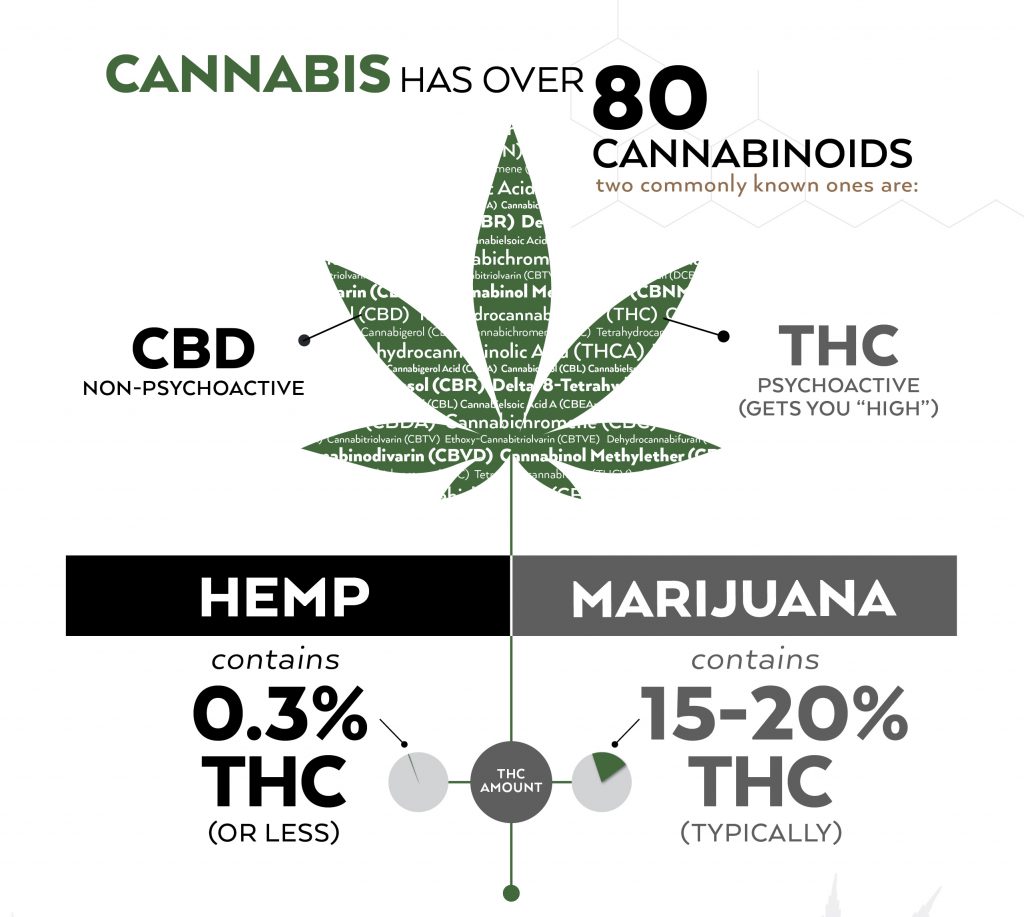
The cannabis plant is loaded with hundreds of cannabinoids, and CBD is one of them. By federal definition, CBD products are legal when CBD is obtained from cannabis plants that contain less than 0.3 percent THC. These plants are called industrial hemp plants to distinguish them from marijuana plants. However, CBD is also present in marijuana plants that contain high amounts of THC, and that is why people get confused about the difference between CBD and THC legality.
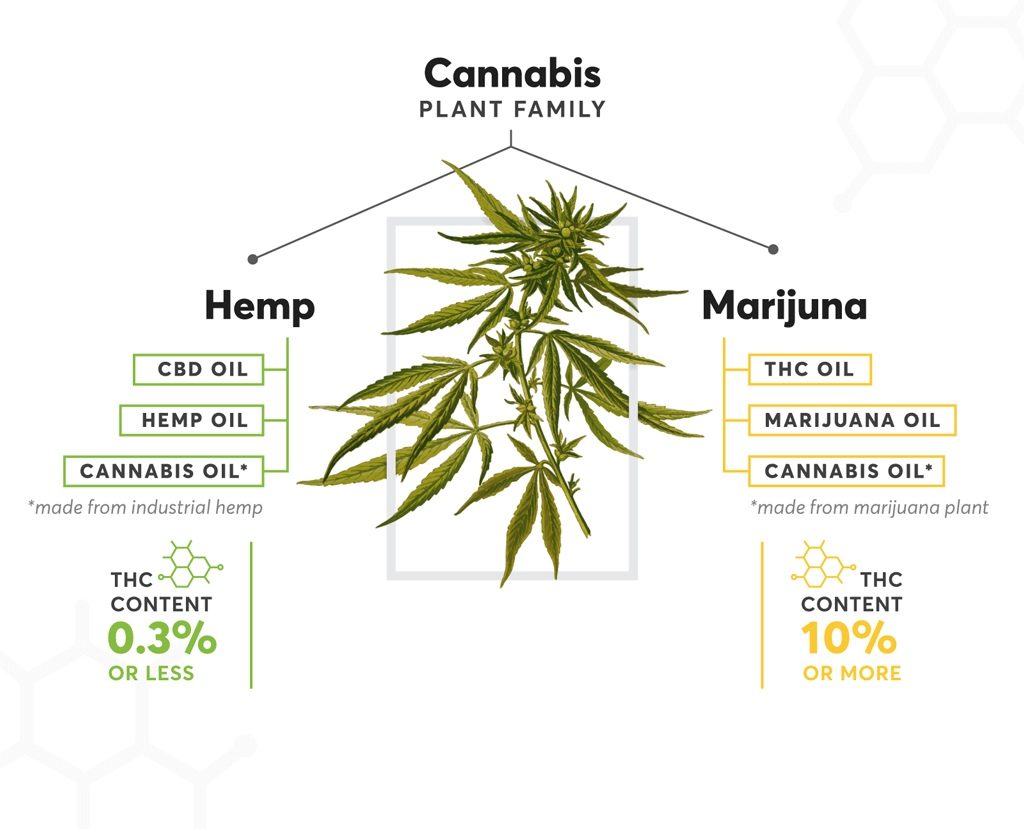
CBD is the acronym for cannabidiol and is the most abundant phytocannabinoid in the industrial hemp plant. Unlike THC, it is a natural compound with no psychoactive properties and is not addictive. CBD interacts with the endocannabinoid system, a master control system regulating most of the body’s processes to keep them in balance (homeostasis), including the feelings of discomfort, sleep cycle, hunger and the immune response.
The endocannabinoid system is found in the central nervous system (CNS) and the peripheral nervous system (PNS). The CNS includes the brain. There are two sets of cannabinoid receptors, called CB1 and CB2, that coexist as regulators in the endocannabinoid system. CBD is a modulator rather than a binding compound, and while it affects both CB1 and CB2 receptors, it primarily influences the CB2 cannabinoid receptors. CB1 receptors are found mainly in the brain, while CB2 receptors are primarily in the PNS. The CB2 cannabinoid receptors manage systems like the immune system and digestive system.
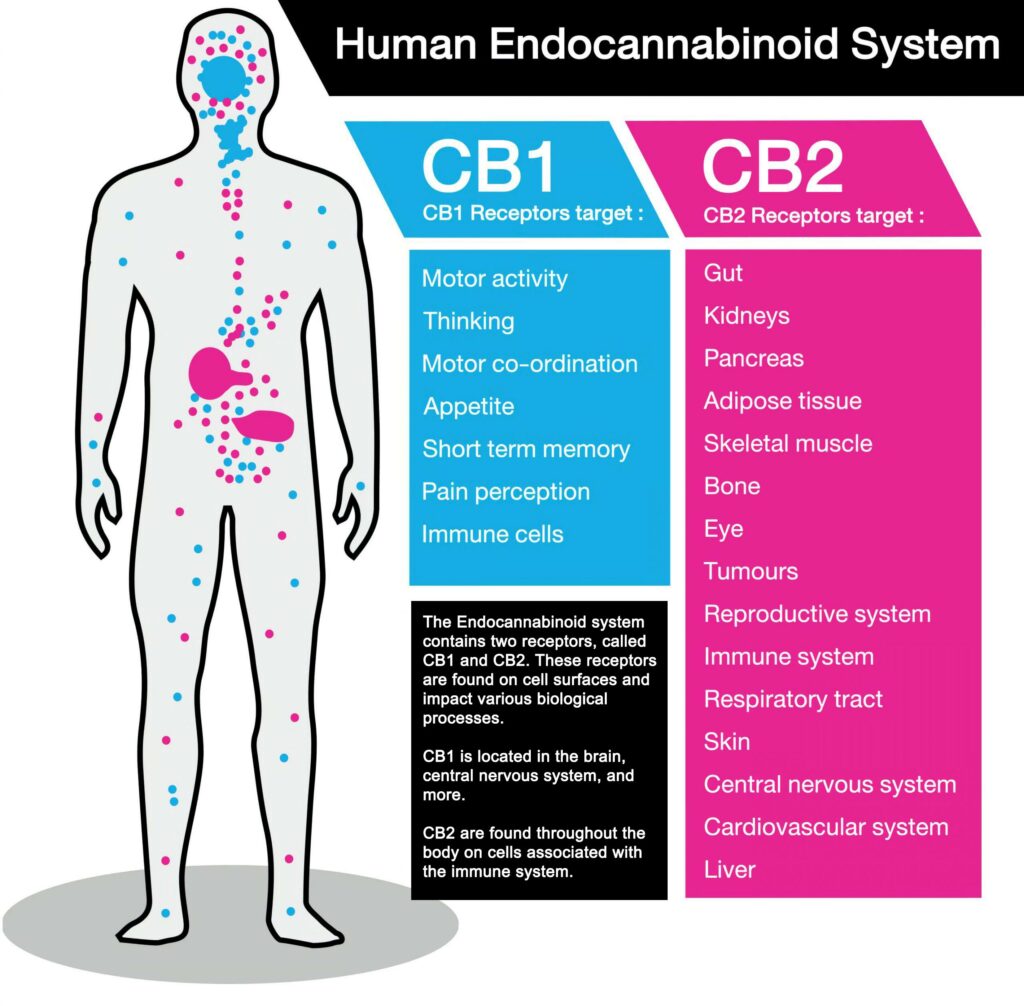
CBD is believed to perform two functions. One is to act as a reuptake inhibitor of endogenous (naturally formed) cannabinoids 2AG and anandamide, which means the natural cannabinoids can remain on cell surfaces longer to activate cannabinoid receptors CB1 and CB2. The natural cannabinoids are not broken down by the metabolism as fast if not for the presence of CBD.
Instead of binding to the CB1 and CB2 cannabinoid receptors, the second function is that CBD modulates the signal the CB1 receptors issue when activated by endocannabinoids and augments the CB2 receptor signaling, which means CBD may trigger a response in the immune system. Medical researchers have also found CBD may reduce feelings of fear.
What is THC?
THC (tetrahydrocannabinol) is a cannabinoid that is naturally abundant in the marijuana plant. Marijuana plants are the cannabis plants that are the main source of THC, and they also have CBD in a smaller quantity. The legal THC in CBD products is extracted from the industrial hemp plants that have less than .3% THC, so CBD products with THC will not produce a high.
THC binds to both CB1 and CB2 receptors in the endocannabinoid system. CB1 receptors are found mainly in the brain and spinal cord but are also found in a smaller number in the rest of the central nervous system. They manage the release of various neurotransmitters, including those that produce the psychoactive effect (high). THC is an agonist (activator) of CB1 receptors which is why it is psychoactive, creating the “high” people seek when consumed in adequate amounts by activating the “reward system” in the brain.
How are CBD and THC Different?
CBD has a low affinity for the CB1 receptors, so it does not produce a high. It prevents the metabolism (breakdown) of endocannabinoids. Researchers also report that CBD may moderate the impact of THC by fine-tuning the CB1 signals prompted by endogenous cannabinoids and THC. At the same time, it increases CB2 signaling as a response. Since CBD affects the brain’s reward system, it is also being studied as having the potential to reduce cravings for opioids.
In the endocannabinoid system, THC binds to CB1 and CB2 receptors and activates the brain’s reward system neurons, affecting perceptions of pleasure, appetite and more. The activation of the CB1 receptors, in particular, increases the release of the “feel good” dopamine chemical. THC mimics the endogenous anandamide cannabinoid, the messenger molecule that affects mood, fertility, memory and appetite.
Benefits of CBD and THC Together
Full spectrum CBD products are made with whole cannabis plant extracts. Thus, they contain CBD and THC. Some of the benefits of CBD and THC together may include the following.
1. Sleep
Since CBD oil may reduce feelings of discomfort and tension, and THC helps strengthen the interaction of CBD with CB1 receptors affecting mood, one of the benefits of CBD and THC together is sleep improvement. The cannabinoids may help relax the mind, making it easier to fall and stay asleep and experience deeper sleep.
2. Discomfort Reduction
Research has shown very promising results indicating that CBD and THC may reduce discomfort. Various studies have found that CBD combined with THC can ease discomfort and may help with enduring discomfort.
3. General Wellness
Combining CBD and THC improves general wellness because the benefits of both cannabinoids are delivered. Studies on the entourage effect have found that taking whole plant extract, which includes terpenes, may create a better outcome than taking each cannabinoid alone. Some potential benefits include more energy, muscle relaxation, improved mood, better sleep and more, all of which are important to general wellness.
4. No Unwanted High
CBD counteracts THC, so any potential psychoactive response is reduced. However, the amount of THC in full spectrum CBD products is less than .3%, so there is no high experienced. This is important to people who want to enjoy the benefits of THC but do not want to get high.
5. Relaxation
CBD promotes relaxation in the CNS. THC can have a sedative effect that includes muscle relaxation. Since CBD is an antagonist to THC, a balance is achieved.
Does CBD Work Without THC?
CBD does work without THC. People who want to avoid any chance of experiencing a psychoactive experience from THC may decide to use a broad spectrum CBD oil because it does not have any THC. The entourage effect is due to CBD, other cannabinoids, terpenes and flavonoids retained in the final product. Other cannabinoids include CBG and CBN. THC-free CBD products are very popular.
FAQs
The entourage effect is the theory that cannabinoids working together produce more significant results. In the entourage effect, CBD taken with THC and other cannabinoids and natural compounds creates beneficial effects not achieved when taking CBD alone. The compounds act synergistically.
As explained, THC is psychoactive. CBD is not psychoactive, and research indicates it may reduce some of the psychoactive effects of THC. CBD also reduces some of the side effects of THC, like increased appetite. If consuming full spectrum CBD gummies, you are already mixing CBD and THC. It is important to understand that CBD and THC taken separately or mixed will affect each person differently.
The broad spectrum CBD products are either THC-free or the amount of THC is negligible. THC-free products are labeled as such. Isolate CBD is pure CBD and is THC-free. Millions of consumers take CBD without THC and report excellent experiences.
Summary
CBD and THC each deliver benefits through their actions in the endocannabinoid system, but the actions differ. Though there is a need for a lot more research, studies on the mixing of CBD and THC find that cannabinoids work together to produce various positive effects. Researchers are studying CBD and THC as potentially therapeutic for various issues. The key to determining if a full spectrum CBD oil can meet your needs is buying and trying a high-quality, low potency full spectrum CBD oil and assessing how your body responds.
Sources
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8221009/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6486906
- https://www.projectcbd.org/cbd-endocannabinoid-system
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6486906/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC6390812/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8116407/ and https://www.med.upenn.edu/cbti/assets/user-content/documents/The%20role%20of%20the%20CB1%20receptor%20in%20the%20regulation%20of%20sleep..pdf
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC2503660/ and https://www.sciencedaily.com/releases/2021/07/210714110455.htm
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC9081504/
- https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30624194/ and https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC8704602/
- https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/pmc/articles/PMC5719112/
Share this post


0